CompTia A+ Notes
Objectives Link
1.0 Mobile Devices
1.1 Laptop Hardware
Batteries – Most modular and easy to replace, some not, specific to model
– Lithium Ion, has no “charge memory”, diminishes max with each charge
Keyboard – Can be easy to replace, typically a few screws and a cable1
– Normally not full size and has function key that preform additional actions
– Keys are fragile, but can be replaceable
Memory – Small Output Dual In-Line Memory Module (SO-DIMM)
– Often easy to replace, but can be soldered
Storage – Older can be HDD, newer have SSD, all are 2.5″, many have M.2
– Replacing depends on model, may have cover or need to remove whole back
Migration – Install OS and Move Data, Image\Clone Old,
– Moving Data is time consuming
– Cloning requires special software, can be drive to drive with no intermediate system
Bluetooth\802.11 wireless – Built in in newer Laptops
– Mini PCI or Mini PCI Express modules used in older laptops
Biometrics – Used for Authentication
– Can use Fingerprint or Face, requires additional configuration to use
Near Field Communication – NFC, short distance networking
1.2 Laptop Displays
Portable LCD – Light shines though liquid crystals, lightweight, low power, inexpensive, black levels challenge for color, Requires separate backlight
OLED – Organic compound emits light, thin and light, no glass, no blacklight, good color, high power and money cost, degrades decayed images on screen
Wi-Fi antennas – Wi-Fi main and aux, Bluetooth, wrap around screen, top of screen
Fluorescent vs LED Backlight for LCD – LED newer and less power and thinner
Inverter – If screen goes bad but has fait image, may be inverter
Digitizer – Enables a stylus or finger to interact with Laptop
1.3 Laptop Features
Function Keys – Has features linked to function keys activated via pressing FN and function key, ie Display, Audio, Media, Backlight and other settings
Dock – Extends the amount of usable Ports
Hardware Security – Kingston Locks
Rotate Screen
1.4 Mobile Devices
Tablets – 7″ or lager screen, designed for touch interface
Smart Phones – 3.5 – 7″ screen
Wearable Tech – Wearable device, Watch, Fitness Monitor
Virtual Reality – Only Virtual world
Augmented Reality – Add digital information to real world
E-Reader – Read books, maybe music, wireless
GPS
1.5 Mobile Device Connections and Accessories

Mobile Device Connectors
Micro-B for EU Devices
USB-C – 24 pins, Includes Audio output, USB 3.1 or 2.0
Lightning – 8 pin Higher power output than Micro-USB
Tethering – Connect phone to computer and use Phone’s internet
Hotspot – Connect to phone via Wi-Fi to use phone’s internet
NFC – Near Field Complication, Small amounts of data, access token/identity card
Bluetooth – PAN (Personal Area Network), Connect without wires
IR – Infrared, Used to control entertainment centers (TVs)
Accessories
Headset – Earphones and microphone, Wired or Wireless, TRRS (Tip, Ring, Ring, Sleeve) or TRS (No Microphone)
Speakers
Game Pad
Extra Battery Pack
Cases/Screen Protector
Credit Card Readers – Point of Sale
Storage – SD/Micro SD cards
1.6 Mobile Device Connectivity
Wireless – Hotspot, Tethering, Airplane Mode, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth
Bluetooth – PAN, 10 Meters, Pair device
Baseband radio – Allows communications with cellular network
PRL – Preferred Roaming List, Connect to correct tower
PRI – Product Release Instructions, Radio settings, ID Numbers, Network Codes, Country Codes
IMEI – International Mobile Station Equipment Identity, Every phone has a different one, allow or disallow device
IMSI – International Mobile Subscriber Identity, SIM Card, Identifies User
VPN – Virtual Private Network, Connect to VPN or create an endpoint
Email Configurations
POP3, IMAP – Receiving
SMTP – Sending
SSL – Secure Socket Layer
POP3 – Post Office Protocol 3, Downloads then, optionally, deletes from server
Default Ports:
POP3 tcp/110
POP3S (SSL) tcp/995
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol, Access Mail, Mail stored on server
Default Ports:
IMAP tcp/143
IMAPS (SSL) tcp/993
SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, Send Mail to a server
Default Ports:
SMTP (No Auth) tcp/25 *Mostly Unused
SMTP (Auth) tcp/587
1.7 Mobile Device Synchronization
Cloud Sync – Hands Off, Wifi/Network connection
Desktop Sync – Lost of Local Storage needed
Automobile Sync – Extend Phone Functionality to car
2.0 Networking
2.1 IP and Common Ports
IP – Internet Protocol
TCP – Transmission Control Protocol
UDP – User Datagram Protocol
TCP and UDP are Encapsulated by the IP protocol, OSI Layer4 (Transport Layer)
Multiplexing – Use many different applications at the same time
TCP
Connection Oriented
– Formal connection setup and close
“Reliable” delivery
– Can manage errors
Delivery Confirmation
UDP
Connectionless
– No Formal open and close
“Unreliable” delivery
– No error recovery
Information is one way
IP Address is like a house address
Port Numbers are like different rooms in the house
IPv4 Socket
– Server/Client IP Address, Protocol, Server Application/Client port number
Non-ephemeral ports (Permanent port numbers)
– Ports 0 to 1023
Ephemeral Ports (Temporary port numbers)
– Ports 1024 to 65535
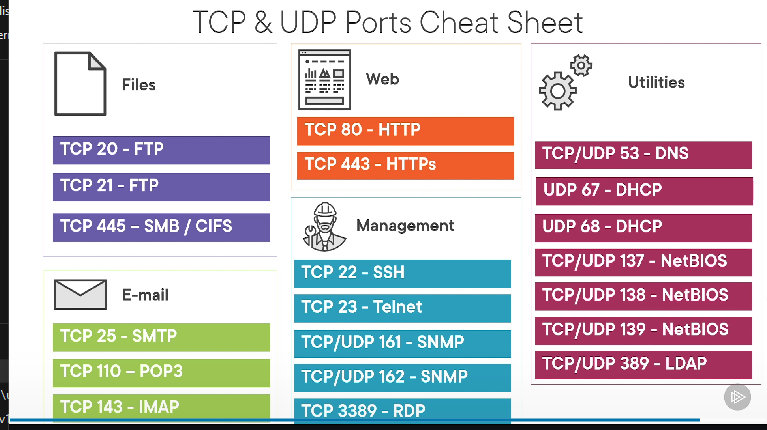
Common Ports
FTP – File Transfer Protocol
TCP/20 (active mode data)
TCP/21 (control)
SSH – Secure Shell (Encrypted)
TCP/22
Telnet – Telecommunication Network
TCP/23
DNS -Domain Name Service
UDP/53
HTTP (HTTPS) – Hypertext Transfer Protocol
TCP/80
TCP/443 (Encrypted)
RDP – Remote Desktop Protocol
TCP/3389
SMB -Server Message Block (File/Printer Sharing on Windows)
NetBIOS
udp/137 – NetBIOS name services
udp/138 – NetBios Datagram service
tcp/139 – NetBios Session service
tcp/445 – Direct SMB NetBios
AFP – Apple FIling Protocol
tcp/548
SLP Service Location Protocol
tcp/427
udp/427
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
udp/67
udp/68
LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (Storing Credentials, Active Directory)
tcp/389
SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
udp/161 Queries
udp/162 Traps
2.2 Network Devices
Network Interface Card (NIC)
– Used to connect to a network, wireless, wired, etc.
Repeater
– Receive signal, regenerate, reset
– Used to extend range or change cable type
Hub
– Traffic going into one port goes out all the others
– “Multi-port repeter”
– Half-duplex, only one device can send information at a time
– 10 meg / 100 meg
Bridge
– Decides where to forward traffic based on MAC address using software
– 2 to 4 port switch
Switch
– Bridging done in hardware
– Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC)
– Many ports and features
– Can be multilayer (Layer 3) if it can forward traffic based on IP
Unmanaged Switch
– Few Options
– Cheap
– No VLAN’s
Managed Switch
– Interconnect with other switches via 802.1Q
– Traffic Proprotozation
– Redundancy with Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
– External Management, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
– Port Mirroring, capture packets
Routers
– Makes forwarding decisions based on IP address
– Connects divers network types, LAN, WAN, copper, fiber
Wireless Access Point
– Not a router
– Wireless Bridge
Wireless Lan Controller
– Centralized management of Wireless AP’s
– Can be cloud based
Firewall
– Filters traffic by port number (OSI layer 4) traffic
– Can encrypt traffic into and out of the network
– Can proxy traffic
– Can be a layer 3 device (router)
Cable Modem
– Connect to Broadband
– Uses DOCSIS (Data Over Gable Service Interface Specification
DSL Modem
– Used over phone lines
– ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line)
– Max Distance 10,000 ft
– The closer you are the faster it is
Power over Ethernet (POE)
– Provide Power and Network over one wire
– Can power low power devices
– Power can be injected or come from switch (POE Switch)
POE Switch
– Ports provide power and network
Ethernet over Power (EOP)
– 500 meg
– Also called Power-line communication (PLC), IEEE standard 1901
2.3 Installing a SOHO Network
SOHO Router
– Cheap, All-in-one device
– Router, Switch, Wireless AP, Firewall, etc.
– Not much to configure
NAT (Network Address Translation)
– 20 billion devices, but only 4.29 billion supported with IPv4
– Source NAT or PAT (Port Address Translation) all internal devices translated to single external IP
Port Forwarding
– Allows internal services to be accessed externally
– Destination NAT
– Changes requests from external devices to an internal IP based on the port number
UPnP (universal plug and Play
– Allows network devices to automatically configure and find other network devices
Wireless Channels and Encryption
– Use highest encryption available
– Use open frequency
QoS (Quality of Service)
– Can Prioritize network traffic based on MAC, Port, or Application
2.4 Wireless Networking
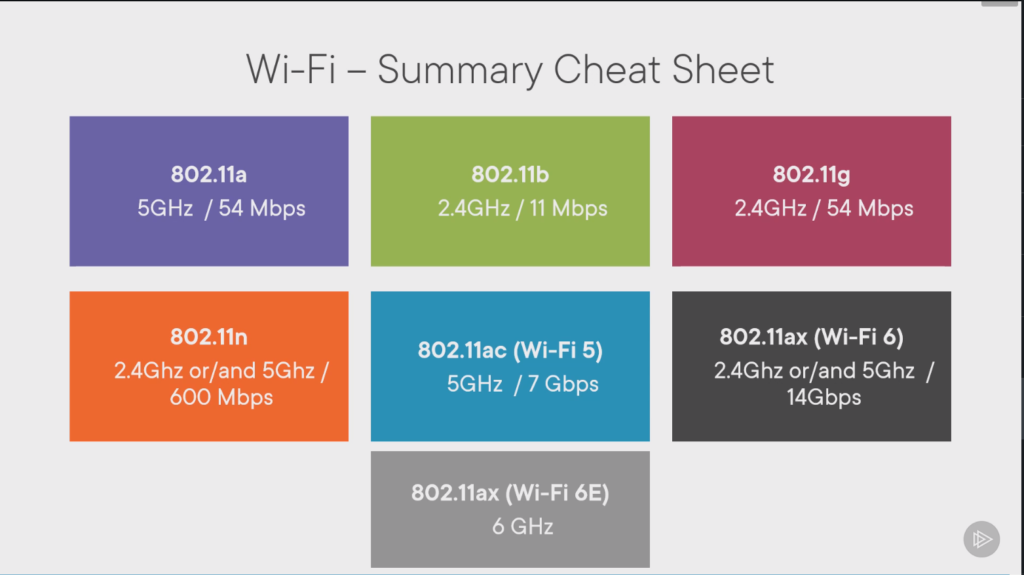
Wireless 802.11 standard
– Managed by IEEE LAN/MAN
802.11a
– One of the first standard released Oct 1999
– 5 GHz Range (1/3 the distance of 802.11b/2.4 GHz)
– 54 Mbit/s
802.11b
– One of the first standard released Oct 1999
– 2.4 GHz Range
– 11 Mbit/s
– Lots of conflicts due to many devices using same range
802.11g
– June 2003
– Update to 802.11b and backwards compatible
– 54 Mbit/s
802.11n
– Oct 2009
– Updates all previous versions
– Runs on both ranges
– 600 Mbit/s
– MIMO (Multiple-input multiple-output) via multiple transmitting and receiving antennas
802.11ac
– Jan 2014
– Updates 802.11n
– 5 GHz Range
– Larger Bandwidth (Channel Bonding), Faster Data Transfer(Signal Modulation)
– Eight MU-MIMO (MultiUser MIMO)
– Almost 7 Gbit/s
| Frequencies | Maximum MIMO Streams | Maximum Theoretical Throughput (per stream) | Maximum Theoretical Throughput (total) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 5 GHz | Not Applicable | 54 Mbit/s | 54 Mbit/s |
| 802.11b | 2.4 GHz | Not Applicable | 11Mbit/s | 11Mbit/s |
| 802.11g | 2.4 GHz | Not Applicable | 54 Mbit/s | 54 Mbit/s |
| 802.11n | 5 GHz and/or 2.4 GHz | 4 MIMO | 150 Mbit/s | 600 Mbit/s |
| 802.11ac | 5 GHz | 8 MU-MIMO | 866.7 Mbit/s | ~6.8 GBit/s |